The Establishment of Company in Indonesia
Authors
General Overview
The establishment of a company is governed by Law No. 40 of 2007 concerning Limited Liability Company as lastly amended by Government Regulation in lieu of Law No. 2 of 2022 concerning Job Creation (“Company Law”). According to Article 1 paragraph (1) of the Company Law, Limited Liability Company is a legal entity constitutes a capital alliance, established based on an agreement, in order to conduct business activities with the company’s authorized capital divided into shares (“Company”). There are two types of companies in Indonesia, namely local company and foreign investment company. The local company is a company which has minimum 2 (two) Indonesian individual(s) or Indonesian legal entity(ies) (or any combination thereof) (“Local Company”). However, the Foreign Investment Company (Perusahaan Penanaman Modal Asing or “PMA Company”) is minimum 2 (two) shareholders which has 100% foreign-owned or joint venture with Indonesian partners.
In addition, the establishment of PMA Company must pay attention to the provisions stipulated in Law No. 25 of 2007 concerning Investment as lastly amended by Government Regulation in lieu of Law No. 2 of 2022 concerning Job Creation (“Investment Law”) and regulations made by the Capital Investment Coordinating Board (Badan Koordinasi Penanaman Modal or “BKPM”).
The registration of Company conducted through the Online Single Submission Risk Based Approach (“OSS-RBA”) system managed by BKPM. OSS-RBA is an integrated system where companies are granted a business license from the government, ministries, and/or agencies to start and run their business activities that are assessed based on the level of business activity risk, as stipulated in Government Regulation No. 5 of 2021 concerning Implementation of Risk-Based Business Licensing (“PP 5/2021”). The implementation of the OSS-RBA aims to improve the investment ecosystem and business activities through the more effective and simple issuance of business licensing; and supervision of transparent, structured, and accountable business activities in accordance with the provisions of laws and regulations.
Name of PMA Company
According to Article 16 of the Company Law, both PMA and Local Company’s name must fulfilled the following requirement, among others:
- in Latin alphabet;
- has not been used by other company;
- does not contravene with public order and/or moral;
- not same or similar with state authority’s name, government authority’s name, or international authority’s name, unless granted by the relevant authority;
- not consist of number or series of number, letter or series of letter that do not form a word;
- in accordance with the objectives and purpose (line of business) of the company, in the event that such line of business is used as the name of the company; and
- The name of a company must begin with the phrase of “Perseroan Terbatas” or “PT”.
Line of Business
A company must have objectives and purpose (line of business) and it will be stated in its Articles of Association (“AOA”). The line of business must be listed in the Indonesian Business Classification (Klasifikasi Baku Lapangan Usaha Indonesia or “KBLI”). Currently the prevailing KBLI is KBLI 2020. Moreover, the investment requirement of PMA Company will be determined according to the line of business of the company. As information, KBLI is usually revised at least in 3 years considering that KBLI 2017 was applied before KBLI 2020.
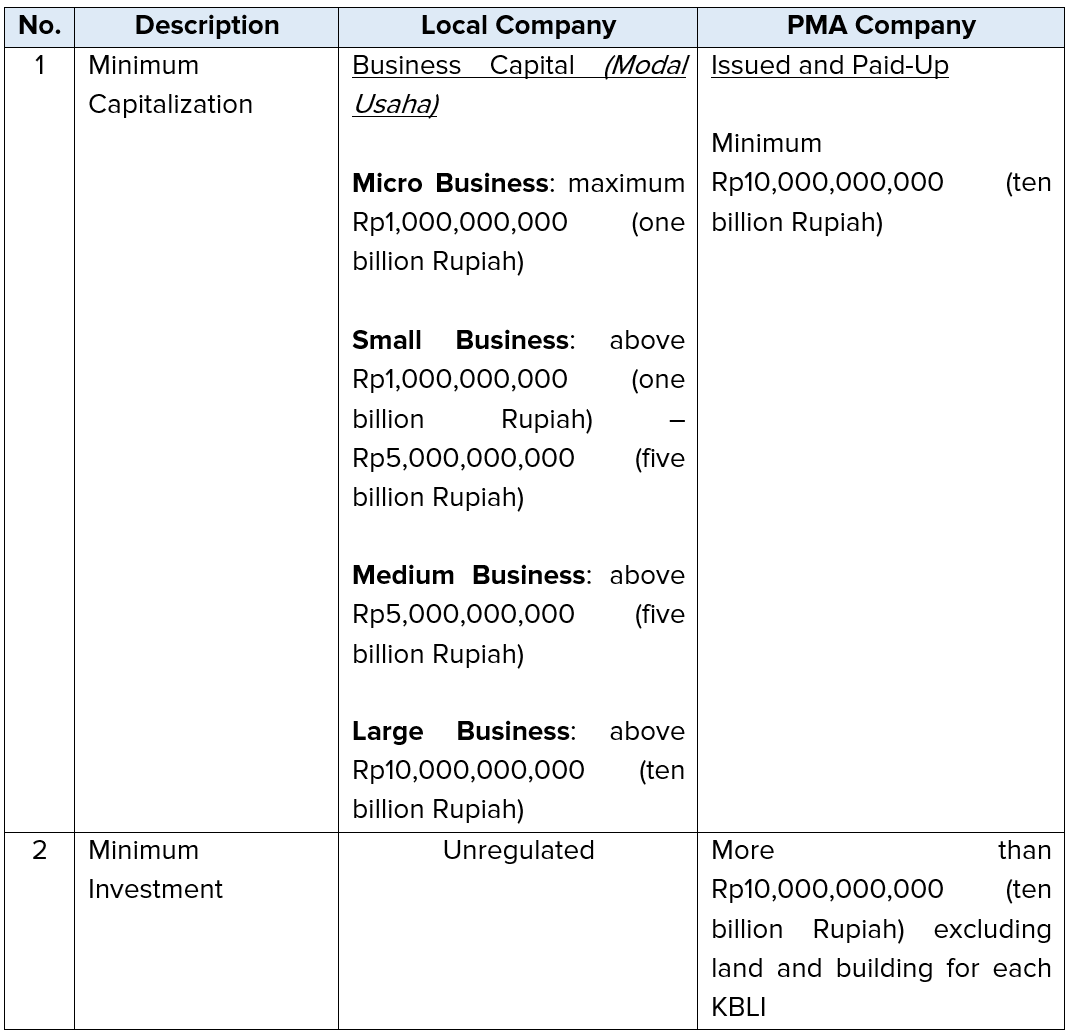
Capitalization
Company’s capitalization consists of (i) authorized capital; (ii) issued capital; and (iii) paid-up capitalThe amount of issued capital and paid-up capital must be equal and the amount of the issued and paid-up capital must be at least 25% (twenty five percent) of the authorized capital (excluded for Micro, Small and Medium Business).
Below are the key differences of capitalization between Local Company and PMA Company:
Organ of a Limited Liability Company
PMA and Local Company comprise of 3 (three) organs: (i) General Meeting of Shareholders (Rapat Umum Pemegang Saham); (ii) Board of Directors (Direksi); and (iii) Board of Commissioners (Dewan Komisaris).
General Meeting of Shareholders (“GMS”) GMS has authorities that are not granted to the Board of Directors or the Board of Commissioners, which are among others as follow:
- Amending AOA;
- Appointing and dismissing members of Board of Directors or Board of Commissioners;
- Approving work plan of company; and
- Approving acquisition, liquidation, dissolution, spin-off, or other corporate actions.
Board of Directors (“BOD”)
BOD is a company organ that authorize and responsible of the management of a company for the best interest of company with good faith and full responsibility, according to the company’s objective and purpose. BOD also act as the representative of the company, inside or out of the court according to the company’s AOA.
BOD consist of 1 (one) person or more Director. If there are more than 2 (two) Directors, the distribution of duty and authority between the members will be determined based on GMS resolution or BOD Meeting resolution. Further, one of them shall be appointed as the President Director.
BOD member is appointed by GMS resolution for certain period of time and such period can be extended. However, foreign citizen are not permitted to hold the position of personnel director, according to the Decree of Minister of Manpower Decree No. 349 of 2019 concerning Certain Positions Prohibited from Being Occupied by Foreign Workers (“MoM Decree 349/2019”).
According to Article 92 paragraph (1) of the Company Law, the BOD duties and responsibilities are to carry out the management of the Company for the benefit of the Company and in accordance with the Company's purposes and objectives (fiduciary duty). In this regard, the BOD of a company that performs fiduciary duties is obligated to carry out their duties and responsibilities as specified in the Company Law and the AoA as well as possible, honestly, in good faith, and in the interests of the company in accordance with the company's aims and objectives.
Board of Commissioners (“BOC”) According to the Company Law, BOC’s duty is to supervise the management policy, management in general, and give advice to the BOD according to the company’s objective and purpose.
BOC consist of 1 (one) person or more Commissioner. For BOC that have more than 1 (one) member, each member shall not act individually, but must be based on resolution of BOC Meeting. BOC member is appointed by GMS resolution for certain period of time and such period can be extended.
According to Article 106 paragraph (1) and (2) of the Company Law, the BOC has the authority to temporarily dismiss BOD members by sending a written letter stating the reasons for his dismissal.
Disclaimer:
This client update is the property of ARMA Law and intended for providing general information and should not be treated as legal advice, nor shall it be relied upon by any party for any circumstance. ARMA Law has no intention to provide a specific legal advice with regard to this client update.
Related Updates
Latest Updates


